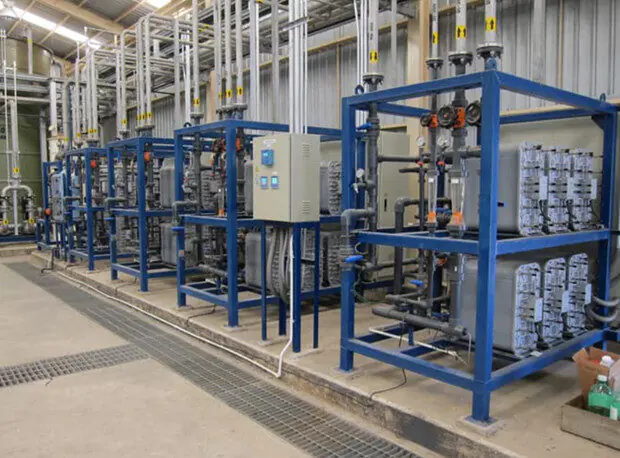
Electrodeionization (EDI) is an electrically driven water treatment technology that uses electricity, ion exchange membranes, and resins to remove ionized species from water.


Ion exchange in the EDI system is continuously generated, unlike resin-based demineralization systems. Typically, product water resistivity of >15 MΩ.cm is consistently achieved using this process. In addition to the advantages of practical operation and reduced downtime during regeneration, EDI can also provide more consistent product purity levels than resin-type ion exchange systems.

Advantages of EDI technology over Mixed Bed Deionization:
- No chemical for regeneration required
- Much lower downtime - proven technology
- Guaranteed consistent output quality and flow
- Reduced health and environmental risks
- Less footprint
- Lower operational costs in terms of chemicals and labor cost
- Continuous process, not batch process
Disadvantages of the EDI system over Mixed Bed Deionization:
- Stricter input quality criteria
- Relatively higher initial investment costs, but with a short payback period due to its low operational cost
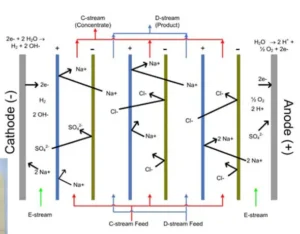
How does EDI produce such pure water?
Diagram 1
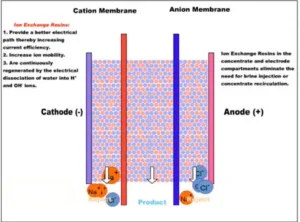
Diagram 2